Definition of pumping parameters for optimization is done by selecting Optimization Data > Optimization Data in Model Tables > Efficiencies/Runtimes (Pumps). This option allows the user to specify which pumps should be considered and how their present value (PV) of energy cost should be taken into account during the optimization.
The optimization pumping parameters are data associated with each pump in the system. The Efficiencies/Runtimes (Pumps) menu option therefore gives access to the regular Pump table, where other system data such as the pump curve can and should have been entered already.
When entering the Pump table, the scrolls to the column “Opt Efficiency(%)”. The 5 other columns related to optimization follow, namely “Opt Time Running1 (%)” to “Opt Time Running5 (%)”. The “Opt Efficiency(%)” column refers to the wire-to-water efficiency of the pump, and the "Time Running (%)” columns to the percentage of time in a specific year, that the pump would be required to operate under the corresponding load cases specified.
At first entry into this Pump table, all the pumps in the system are listed with 100% wire-to-water efficiencies in the first column and 0% run-times under the columns of each active load case. The 0% run-times will of course result in zero pumping cost, with the effect that energy cost will not be considered in the optimization. This can be changed by over-typing with the appropriate run-times.
Pumps are assumed to operate with the characteristics curve specified as part of the system data unless continuity dictates the flow rate of the pump (no reservoirs or tanks on the downstream side of the pump). In this latter case the characteristic curve is ignored and the head is selected such that the minimum pressure requirement downstream of the pump is exactly met.
The present value (PV) of energy cost for each pump is calculated as follows, for each combination of candidate diameters:
•The pumping head and flow (H and Q) under each load case is determined.
•The energy required for pump operation for each load case is determined.
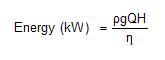
where
ρ = Mass density of the liquid
g = Gravitational acceleration (9,81m/s²)
Q = Pumping flow rate (m³/s)
H = Pump head (m)
η = Wire-to-water efficiency of pump (as specified in optimization data)
•The number of hours that the pump runs each year under every load case is determined by multiplying the run-time percentage with the number of hours per year.
•The annual energy consumption (kWh) for each pump is calculated by multiplying the number of hours it runs under each load case with the energy required for pump operation under the load case, and summating separately for all the load cases.
•The annual energy cost is the product of the annual energy consumption and the R/kWh cost of energy.
•The PV of energy cost is then determined by discounting the annual cost at the given discount rate and over the given term.
Since the "Pump Efficiency and RunTime editor" is the same table as the Pump table, it has the same special editing functions, sorting functions, customization possibilities and exporting facilities.
(The Pump Efficiency and RunTimes% are considered system specific data, which is saved as part of the system data.)
The Pump Efficiency and RunTimes% are properties associated with each pump in the system data. Therefore, the Efficiencies and RunTimes% can also be edited directly in the Pump table, or in the Link Info box available in the Albion environment, or by the selective editing features available in the Albion environment.